Home » Posts tagged 'drain cleaning'
Tag Archives: drain cleaning
The Importance of a Reliable Sump Pump
Many homes are protected by a sump pump, an unassuming but crucial device that quietly safeguards properties against flooding and excess moisture. However, even this simple device can be prone to several issues.
A pump overload can damage the pump, and clogged discharge lines are problematic. Thankfully, these problems can be easily addressed with the right maintenance and monitoring. Contact Sump Pump Aurora CO now!
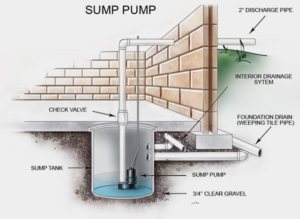
Water-powered pumps offer a reliable backup for home flood prevention. Their operational independence from electricity means they continue to run even when power is cut. Their energy efficiency saves homeowners money on utility costs over time. Unlike battery-powered backup sump pumps, which must be replaced every three years, water-powered pumps last as long as they continue to work properly.
A water-powered pump is powered by your home’s municipal water supply, which is connected to the pump by a valve and a suction pipe. When triggered by a second float switch within the sump pit, positioned higher than the primary pump’s float switch, the water-powered pump uses high water pressure from the municipality to move the municipal water through the pump jet and then discharge it outside your home. Using the Venturi effect, this process causes your municipal water to draw up the collected water from your basement into its flow. It expels it out of your home, without the need for electrical power.
Since water-powered pumps don’t use a battery, they can operate for as long as your home has a continuous supply of municipal water pressure. However, as your house’s plumbing system ages, you may experience reduced water pressure that impacts the performance of your sump pump.
As with an electric backup sump pump, water-powered pumps can require some regular maintenance, such as checking and replacing the battery, ensuring proper electrical connections, and examining motor efficiency. But these routines are much less frequent than those required for battery-powered pumps, which can take up to a full day to complete and can be expensive to replace when batteries degrade.
In addition, water-powered pumps need periodic inspections of their float switches to ensure they are functioning properly. If the float is obstructed, it can cause your pump to continuously run, which can cause the pit to overflow. In most cases, the pump should only run when the float is engaged and the pump’s discharge valve opens, preventing the pit from filling up too high and flooding your home. You may be required to have a backflow preventer installed on your water line so that the pump doesn’t pollute the potable household water supply.
Electric Pumps
When pumping fluids, whether it be oil or water, mechanical pumps are commonly used. However, electric pumps have gained traction for many applications because they are reliable, require less maintenance and generate less heat. Electric pumps can also provide greater flexibility and precision than mechanical ones, especially for applications where the fluid demands are constantly changing, such as lubricating equipment.
Electrical pumps are powered by an electric motor which is connected to the pump suction flange via a shaft. This eliminates the need for a flow control component, saving manufacturing costs. Electric pumps can also be designed to precisely match the pump output to the flow requirements of the machine they are lubricating, reducing energy consumption.
A sump pump is designed to prevent the flooding of a basement or crawl space by pumping out excess water. It is essential that the pump be installed correctly, which is why it’s a good idea to hire a licensed and experienced plumbing contractor for the job. In addition, the pump should be plugged into a dedicated circuit that is not shared with other appliances. This makes it less likely that power will be lost due to a blown fuse or tripped circuit breaker.
There are two main types of sump pumps: submersible and pedestal. While submersible pumps are fully submerged in the water, pedestal pumps have their motor above the sump basin. Pedestal pumps are typically louder and take up more room than submersible pumps, but they offer a number of advantages including easy access for maintenance.
Regular maintenance of a sump pump is critical to its longevity and performance. A flooded basement or water damage can be very costly, and it’s a good idea to have a professional inspect your pump regularly for signs of wear or failure.
Depending on the type of sump pump, there are different maintenance tasks that should be performed to ensure the safety and proper function of the system. Inspecting the pump for leaks is important, as well as ensuring that the weep hole is free from obstruction and that the float switch and pressure switch are working properly.
Low-Voltage Pumps
If you have a basement or crawl space that is prone to flooding, sump pumps are very important in keeping water from building up under your house. This prevents structural damage and keeps the area clean and safe for your family to use. This also protects against mold, wood rot, and pests that could otherwise cause problems for you and your family. In addition, it will help keep the value of your home up and may make it easier to sell in the future.
A sump pump works using a float switch that is activated when the water level rises above a predetermined amount in your sump pit. The switch is connected to an electric motor that uses an impeller to rapidly spin, creating a low-pressure area that draws the water into the pump and then out of your discharge line. The discharge line is cored through your wall and siding, and it drains away from the foundation of your house.
There are a number of different types of pumps available. Some are submersible and others sit on a pedestal above the sump pit and basement water line. Pedestal pumps allow for some of the water to enter the pump and naturally re-absorb into the ground before it is pumped out, which can reduce the frequency that your sump needs to operate.
You can also find pumps that have built-in alarms, automatic switch mechanisms, and adjustable float switches. Some even have silencing check valves that are designed to reduce the noise produced by the pump as it runs. In addition, you will want to consider the quality and durability of the pump when choosing which one to purchase.
You will also need to determine where you will need your pump to drain water to. It is best to discharge it in an area that is downhill and away from your house, but some areas have a difficult time draining because of the composition of the soil or the grade of the land. In these cases, it is best to install downspout extensions so that the water can drain farther away from your house than it normally would without a sump pump.
High-Voltage Pumps
In addition to preventing flooding and water damage, sump pumps help eliminate mold and other organisms that thrive in moist conditions. These organisms can be detrimental to the health of your family and can even lead to serious illnesses such as cancer. In addition, a well-functioning sump pump helps prevent these organisms from spreading into your house, where they can damage electrical wiring and cause fires.
To keep your basement dry, your sump pump is constantly working to remove water from the lowest point of your home – the sumps. It is important to have a well-functioning pump that is large enough to handle the amount of water your property collects. It is also important to have a backup option, such as a battery-powered system or an additional sump, to ensure that the pump will be able to operate in the event of a power outage or during severe storms.
Many residential sump pumps are located in a pit or basin underneath the basement floor, where it is designed to collect the water from the area. This is necessary because water that accumulates in your basement can leak into the foundation of your home and create serious problems such as a sagging floor, structural instability, or even flooding of your entire house. This type of pump is also used in industrial and commercial applications to control ground saturation, which can affect the stability of surface soil and may cause ponding or flooding.
A sump pump is powered by an electric motor, which activates the pump when a float switch rises to the appropriate level of the pumped liquid. Once the float switch is activated, it will power an impeller or small fan-like device that quickly spins to draw the water into the motor and then discharges it through your discharge line. The discharge line is cored through your basement or exterior siding and then runs away from the house, directing the water outside where it will not return to the home.
There are several types of switches available for triggering the pump, including diaphragm pressure sensors and electronic switches that use capacitance or conductance technology to sense changes in water levels. These switches offer more precise control over the activation and deactivation points, and they are less prone to mechanical issues compared to float switches that are attached to the end of a short length of flexible cable, which can get tangled or obstructed in your sump basin.
Methods of Removal
Liquid Waste Removal Perth can cause many problems if improperly disposed of. Consequently, businesses producing this type of waste must follow strict guidelines to comply with regulations.
Through treatment and neutralization, some liquid waste can be recycled or made less harmful, reducing the amount of garbage that needs to be disposed of.

The term “liquid waste” refers to any waste that exists in liquid form rather than gas or solid form. It encompasses a wide range of waste products, including wastewater, fats, oils, and grease (FOG), solvents, chemical liquids, agricultural runoff, and pharmaceutical liquids. Wastes classified as liquid waste have special requirements relating to their storage, transport, and treatment.
Many types of liquid waste can be recycled through various waste management processes. This helps reduce these wastes’ environmental impact and boost business efficiency. Waste breweries, for example, can be turned into animal feed or biofuels by using waste water to wash and separate the beer mash. These non-arduous liquids can also be turned into organic compost that can be used to improve soil quality or as a fertilizer for plants.
Toxic liquid waste, such as effluent from industrial processes, can cause serious environmental problems if improperly handled. This type of waste may contain heavy metals, organic compounds or radioactive materials. It can pollute groundwater and contaminate the surrounding environment, posing a risk to human health and the surrounding ecosystem.
Effective Liquid Waste Management involves a process of assessment, analysis and monitoring that ensures compliance with regulatory standards. The first step in the process is to characterise the liquid waste by conducting a series of tests on it. This allows businesses to identify contaminants and pH levels, which informs the choice of treatment and disposal methods. Regular assessments also help companies track changes in the composition of their liquid waste streams and identify areas where they can improve their practices.
The next step in the process is to treat and dispose of the liquid waste. This can be done through a number of processes, including filtration, neutralisation, chemical treatment and biological treatment. Filtration removes solid particles from the waste stream, neutralization adjusts the pH level, and chemical treatments break down hazardous substances in the liquid waste. Biological treatment, which uses microorganisms to degrade organic matter, is often used in sewage and wastewater treatment. For more difficult wastes, physical treatments such as sedimentation or coagulant usage can be used to separate oils and greases from the liquid waste. Once this step is complete, the liquid waste can be safely disposed of via recycling, land application or anaerobic digestion.
Treatment
Businesses producing liquid waste must have a system in place to store it until it can be disposed of properly. This prevents spillages and leaks that could contaminate waterways or groundwater aquifers. It also prevents the waste from being dumped into the environment, which would not only harm wildlife and soil but potentially put human life at risk if it comes into contact with people. Liquid waste is a very dangerous type of waste and must be disposed of in strict compliance with regulations or face heavy penalties.
Whether it’s sewage effluent from a toilet or washroom, acids and chemicals from factories, hydrocarbon waste or solvents from spray booths, these substances can cause serious environmental damage if they are released into the natural environment without proper treatment. They can contaminate waterways, contaminate agricultural fields and even cause geotechnical problems that threaten public health.
Most types of liquid waste cannot be placed in the general waste stream and must be handled separately by a waste management service provider. This is because they pose a greater risk to the environment than other types of waste, which is why there are very strict rules governing their disposal.
Liquid waste can be treated in a variety of ways, depending on its composition and how it needs to be treated for. Physical treatment techniques, like centrifugation or sedimentation, can be used to separate solids from the liquid and make it easier to handle and dispose of. Chemical treatment is often a part of the process as well. This is used to break down toxins or change the pH level of acidic or alkaline wastes.
Once the liquid waste has been treated, it can be recycled or reused in a number of ways. This can save money and help the environment by reducing demand for raw materials. It can also be injected into deep underground wells, which are isolated from the environment and water supplies, for safe long-term storage.
Finally, evaporation ponds can be used to dispose of non-hazardous liquid waste by allowing the water to evaporate. This can be a cost-effective solution for companies with high volumes of liquid waste that need to be disposed of quickly.
Disposal
The way liquid waste is disposed of has a significant impact on the environment and human health. If it is not disposed of properly, it can damage the natural habitat, kill plants, and pollute groundwater or surface water sources. It can also cause serious gastrointestinal illnesses or heavy metal poisoning in people who drink contaminated water. Therefore, businesses have a duty to prioritize safe and compliant liquid waste disposal.
The first step in liquid waste management is to identify the type and category of the waste. This requires thorough assessments and testing, which can include evaluating contaminant levels, pH levels, and chemical characteristics. This process is called characterization and ensures that the right treatment and disposal methods are used.
After characterization, the liquid waste can be further processed for disposal. This may include filtration, neutralization, chemical treatment, or biological treatment. This treatment process eliminates or reduces harmful pathogens and other contaminants, making the waste safer for storage, transportation, and disposal. The treated liquid waste is then placed into a container for transportation and disposed of according to regulations.
Non-hazardous liquid waste can be disposed of through landfill, which is a simple and cost-effective technique. In addition, it is possible to recycle and reuse some types of liquid waste, such as sludge from sewage plants and wash waters. In the future, this could become more common as businesses seek to minimize their environmental footprint and save on costs.
Other methods for disposing of liquid waste include incineration and deep-well injection. Incineration uses high temperatures to burn the waste, which helps reduce its volume and removes harmful pathogens. Deep-well injection involves injecting the liquid waste into underground wells, which requires suitable geological conditions.
Some facilities can even turn their non-hazardous liquid waste into compost. This method removes the water, which leaves behind organic matter that contains nutrients such as nitrogen, potassium, and sodium. The resulting compost is then used as a fertilizer to help plants grow.
Regulations
Liquid waste disposal is heavily regulated, and tiny infractions can carry hefty fines. Correct handling, storage, and disposal practices are critical to ensuring your facilities are safe for both employees and the environment.
Flammable liquid wastes such as acetone, paint thinner, and chemicals require proper storage and disposal to prevent fires or injuries. The proper disposal of these hazardous materials is regulated by many national, state, and local agencies. Your business should stay updated on the most current regulations and guidelines to ensure you are following the best possible practices and keeping your facility safe for all involved.
Nonflammable liquids such as sewage, household garbage, and other nonhazardous commercial products are also regulated. Regulations apply to generating, storing, transporting, treating and disposing of these liquids.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regulates household, industrial and manufacturing solid and hazardous waste through the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA). RCRA establishes a framework to control these types of waste from the time they are generated until they are disposed of.
These RCRA regulations include defining hazardous waste, collecting, transporting and processing hazardous waste, testing, tracking, and reporting on the generation, storage, transportation, treatment and disposal of these wastes. These regulations are designed to protect our natural resources, reduce toxic chemical pollutants and wastes that threaten the health and safety of people.
In addition to the EPA’s RCRA, the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation (DEC) has their own regulations and guidance documents for managing hazardous waste. These documents include technical and administrative guidance memorandums (TAGMs) and enforcement discretion letters. The TAGMs and enforcement discretion letters help regulated communities better understand how the State implements the federal regulations and how to navigate changes in the RCRA program.
All waste must be stored in containers that are leakproof, durable, easily cleanable, and capable of keeping waste materials away from vectors until they are removed for collection. These containers must be of an adequate size to accommodate all food wastes, rubbish, and ashes that a residence or other establishment generates in the interval between collections.
Waste that is not collected and disposed of properly can contaminate water sources such as rivers, lakes or groundwater. This can have devastating effects on ecosystems and cause the harmful substances to leach into drinking water supplies, posing serious health risks for people and animals. In addition to contaminating water sources, improper disposal of hazardous waste can also pose occupational health hazards for workers. These risks include skin irritations, respiratory problems, and long-term health effects.